Sensors
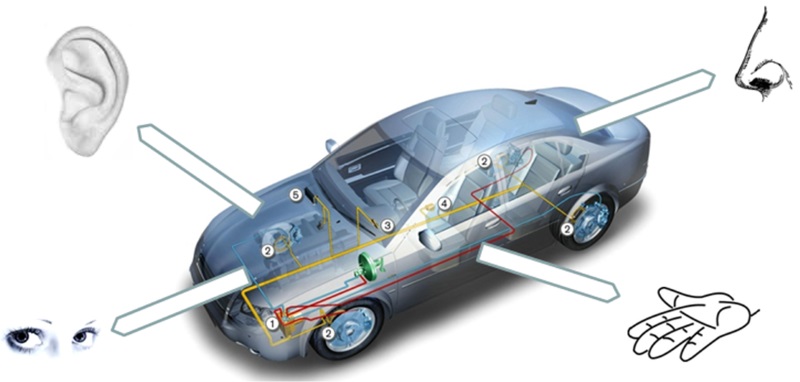
Greater safety, security, comfort, and reduction of exhaust gas emissions on vehicles with easier and faster service enables the use of electronically controlled systems. One of the indispensable elements of electronic control is sensors. They are a kind of “sense” that constantly tracks, monitors, and measures the parameters of various systems on vehicles.
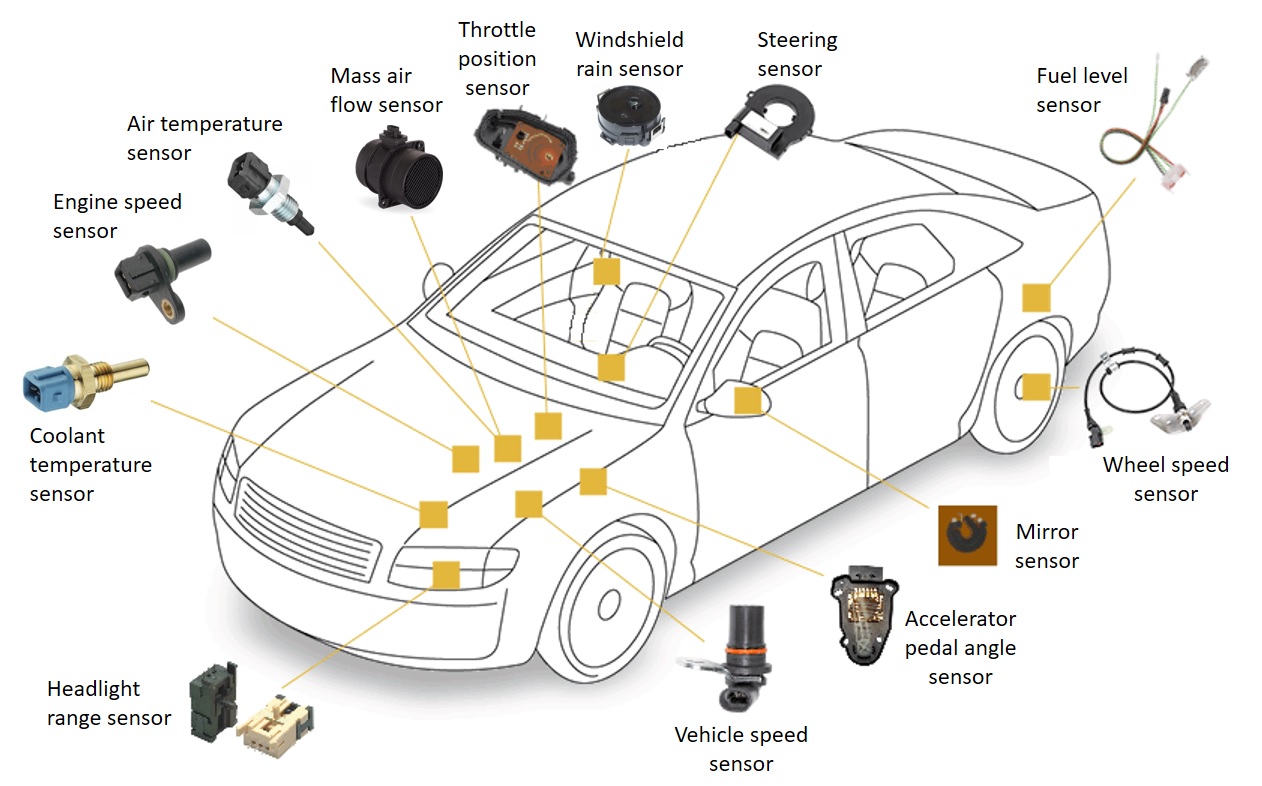
Modern vehicles have a large number of electronically controlled systems whose function is based on sensors. Sensors can be divided based on the measurement quantity that is monitored, measured, and converted into a suitable electrical signal.
There are sensors on the vehicles:
– mode;
– temperature;
– movements;
– position;
– distances;
– direction of movement;
– positions, speeds, and accelerations (angular, linear);
– elapsed time and frequency;
– noise and vibration;
– liquid level;
– pressure (absolute, differential, atmospheric);
– flow;
– number of rotations (rpm);
– forces and moments;
– mechanical stress;
– orientation;
– fluid viscosity;
– electrical voltage and amperage;
– humidity and rain;
– light intensity;
– gas concentrations.
Correct and reliable vehicle operation depends on correct and accurate sensors. The ECU constantly checks the correctness of the sensors during system operation. Also, service technicians check the correctness of the sensors through the vehicle maintenance and repair process. That is why service technicians must have a good knowledge of the role, mode of operation, and procedure of sensor testing. In this section, you will get to know the sensors on vehicles and the procedures for testing, repairing, and replacing them.